Introduction:
The two-wheelers are commonly found on the roads, but the Tri or three-wheelers rarely found in the entire world. There are some countries in which Tri-vehicles, Tri-bikes, and Tri-Cycles are found. Some countries like China, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh have Tri-vehicles. Karl Benz is the inventor of the Tri-Wheeler that made a three-wheel vehicle. Karl and his friend made this car that was famous he made about 350 vehicles in their garage. After that, Karl Benz with his friend made a 4-wheeler vehicle, which was a change in design. There are many two-wheelers, but now we will talk about 3-wheelers and the Inventor of the 3-wheeler who made it for the first time.
| Basic Information | Inventor’s information |
| Name of Inventor | Karl Benz (Karl Friedrich Benz) |
| Nationality | German |
| Date of Birth | 25th November 1844 |
| Place of Birth | Mühlburg, Baden, German Confederation (now Karlsruhe, Baden-Württemberg, (Germany)) |
| Date of Death | 4th April 1929 |
| Place of Death | Ladenburg, Baden, Germany |
| Resting Place | Cemetery of Ladenburg |
| Age | 84 years old |
| School | A local grammar school in Karlsruhe |
| University | Poly-Technical University, The University of Karlsruhe |
| Occupation | Engineer |
| Career | 1868 – 1929 |
| Famous for | The inventor of Benz Company |
| Title | The inventor of Mercedes Benz Firm |
| Other works | Iron Construction Company |
| Projects | Founded Fabrik für Maschinen zur Blechbearbeitung,Gasmotorenfabrik in Mannheim A. G,Benz & Cie |
| Famous Design | Benz Patent Motorwagen |
| Famous Advancement | Petroleum-powered automobile |
| Spouse | Bertha Ringer (m. 20th July 1872–4th April 1929, his death) |
| Children | N / A |
Early Life and Education:

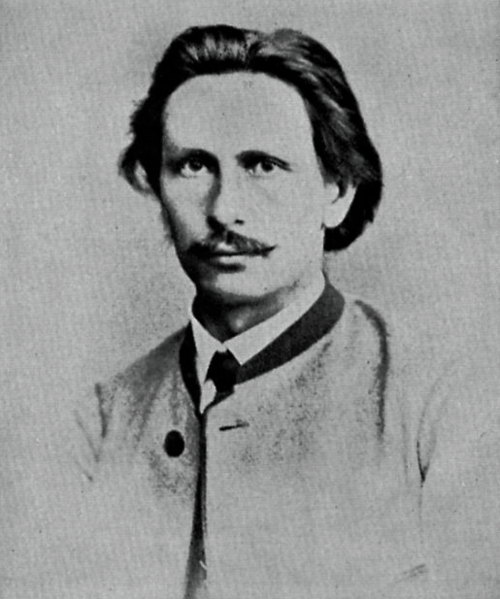
Carl Benz was born on 25th November 1844 in Mühlberg close to Karlsruhe and started Carl Friedrich Michael. He later composed his name only with the letter “C”, which clarifies why the two spellings are found in important writing. Carl’s father, one of the main motor drivers of the Baden State Railways, died under two years after the fact, in July 1846.
Anyhow her modest pay, Carl’s mom figured out how to send him to a language structure school, known as a “Lyzeum” back then, and to fund a course of studies. Carl, who took a deep interest in designing, didn’t have any desire to turn into a government worker as had arranged. In 1860, when he was not yet 16 years of age, he could leave language school for the Karlsruhe Polytechnic, today a college, to plan mechanical designing [1].
Marriage of Carl Benz with Bertha in 1872:
In January 1869 he took up another situation as a chief at the Gebrüder Benckiser designing works in Pforzheim, before moving to the company’s specialized office, where he chipped away at the plan of iron scaffolds.

Quick to have an organization, Carl Benz combined with mechanical designing expert August Ritter to set up the firm “Carl Benz and August Ritter, Mechanische Werkstätte” in Mannheim in August 1871.
It before long turned out to be obvious that Ritter was not a solid assistant and Benz got him out.
He was simply ready to do this with the help of his lady of the hour Bertha Ringer, a technician’s little girl from Pforzheim, who didn’t stop for a second to use her settlement for this reason [2].
Designing of Different Projects:
In the wake of finishing his examinations, from August 1864 to September 1866, Carl Benz labored for a very long time as a fitter, building trains at the designing works of Maschinenbau-Gesellschaft Karlsruhe. It was here he picked up his first commonsense involvement with mechanical designing. In harvest time 1866 Benz joined Waagen and Maschinenfabrik Schweizer, which invented scales and other hardware. Here he was at first applied in the workshop, before being elevated to the degree of “first managerial official” in May 1867, when he functioned as a sketcher and creator [2].
Mechanical Engineering Expertise:
On July 20th, 1872 Bertha and Carl Benz were wedded. In his diaries, Benz later expressed: “In the wedding, a dreamer who understood what she needed regardless, from the inconsequential to the profound joined me”.
Bertha Benz was indeed important to the resulting success of Carl Benz. Strong and creative, she over and over went to flutter for his thoughts and gave her better half significant moving in the entirety of his exercises. In 1873, Eugen, their first youngster, was born. Three little girls trailed their second child Richard (1874: Clara (1877), Thilde (1882), and Ellen (1890).
In past times, Carl Benz’s business went truly, even after he had left Ritter. Bailiffs even seized the shop gear at his “iron foundry and planning workshop”, in July 1877 [2].
Design of Gas Motor and its Working:
It was therefore against a foundation of stresses over his occupation and the striking requests of his ordinary business that Carl Benz set to deal with the gas motor in 1878. He saw the interior ignition motor not just as a capable drive framework for machines, yet in addition as a vital development while in transportation to understanding his vision of a horseless vehicle [2].
Two-Phase Motor Plan:
He was directly in reasoning that the opportunities for building up the barometrical gas motor restricted, and patent DRP 532 ensured the four-cycle motor created by Otto, held by Gasmotoren-Fabrik Deutz since 1877. After extended and troublesome tests, Benz at long last succeeded: his motor ran pleasantly unexpectedly on New Year’s Eve 1879 [2].
With his two-phase motor Benz had made a significant reason for the business achievement of his organization. Planning to build up a sound monetary establishment, he set up the gas motor production line “Gasmotorenfabrik Mannheim” in October 1882 as a stock organization to which he contributed his complete stock and hardware. Benz held a simple 5 percent share and allowed just restricted impact even where specialized issues concerned [2].

Selling of the Gas Motors:
Besides, the chief premium of his financial specialists lay in the trustworthy business of selling fixed gas motors and not, as Carl Benz wrote in his diaries, in his “most loved ideal the engine vehicle”. In like manner, Carl Benz left the youthful organization after only a couple a very long time in January 1883 and got himself in a real sense in the city, as he had submitted his creation offices to the firm and had leased his old workshop [2].
New Financial Specialists Investors:
That very year Benz discovered new financial specialists. Max Rose and Friedrich Wilhelm Eslinger, who sold bikes, besides other things, in their Mannheim exchanging organization, got familiar with Carl Benz through cycling. In October 1883 the three set up the firm “Benz and Cie. Rheinische Gasmotoren-Fabrik Mannheim” as an overall association and put the two-stroke “Framework Benz” motor available. Deliberate creation fired up rapidly in recently prepared manufacturing plant buildings and the normal labor force before long numbered 25[2].
Idea from the Horse Cart to Horseless Vehicle:

For Benz, the business success of the two-cycle motor made sure about the monetary premise on which he could dedicate himself to his vision of the horseless vehicle. Notwithstanding its many benefits, he could not use the two-cycle motor for this. Like the four-cycle motors worked by gastrin-Fabrik Deutz, it was too enormous and too weighty to ever considered as a drive for vehicles.
For the vehicle motor which he presently created, Benz depended on the four-stroke guideline: the acceptability of the Deutz patent DRP 532 had raised doubt about by activities for termination, and in 1884 the Patent Office announced a clear point in the patent invalid and void [2].
Increasing Speed of Tri-Vehicle:
Mike Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach, Carl Benz needed to discover methods of speeding up; and like the pioneers from Cannstatt, he zeroed in consideration essentially on the start and valve control. Although the motor accomplished a speed of “just” 400 cycles for every moment and was hence less productive than Daimler’s plan, it took the force needed to drive a “horseless carrier” [2].
Design with Full Consciousness:
Carl Benz showed his actual capacity not with this motor, but with the vehicle for which he had created it. He was not fulfilled essentially by accepting his motor into a current vehicle, for example, a carriage. Rather, he planned his engine vehicle as a combined development in its own right, whose important component was the motor with a flat chamber and an enormous, even flywheel. Benz planned his additional vehicle as a three-wheeler since it upset him with the single-rotate or drawbar guiding normal in carriages at that point. Carl Benz simply exchanged over to four-wheeled vehicles in 1893 when he had tackled this issue [2].
Unsatisfied and Testing the Engine:
In October 1885, following quite a while of increased work, Benz was at long last ready to finish his engine vehicle and start testing.
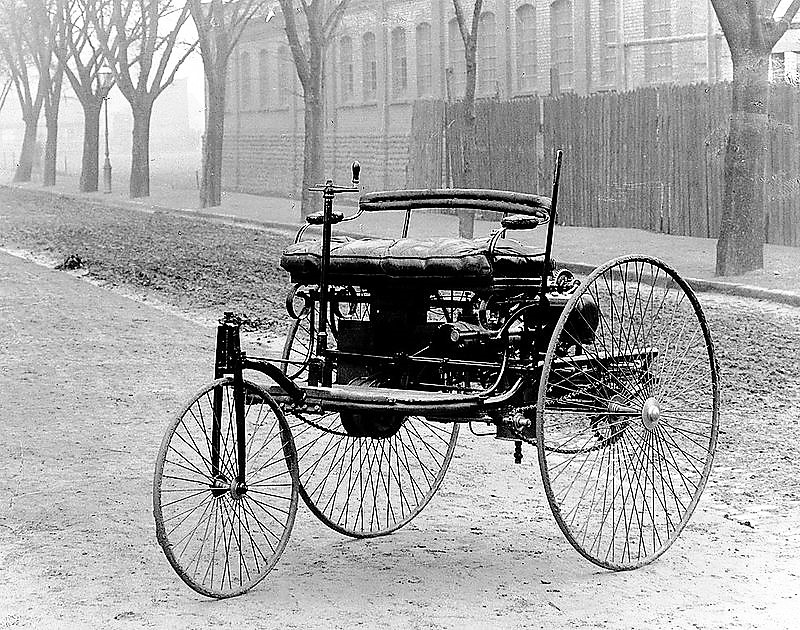

On 29th January 1886, he made a pace which was to leave a mark on the world: he recorded a patent application for his “vehicle with gas motor drive” at the Imperial Patent Office. The patent detail DRP 37 435 was viewed as the birth confirmation of the vehicle and offered to rise to the name “Patent Motor Car” for the world’s first car.
The way to Carl Benz’s wealth was the willpower with which he set about altering his vision into the real world: he had the thought for an engine vehicle, planned it, had it protected, assembled it, tried it, put it available, produced it in an arrangement, created it further, thus made his development usable [2].
Trial and Production of Tri-Wheelers:
The major trial of the vehicle happened in the manufacture line yard. Trips on open streets before long followed in the early morning hours and under the front of mystery. Benz attempted the main recorded ride in July 1886. The Neue Badische Landeszeitung announced in its morning version of July third: “A velocipede running on ligroin gas, planned at the Rheinische Gasmotoren-Fabrik of Benz and Co.–has announced already in these pages—tried early today on the ring street and said to have performed sufficiently. [2]“
Changing of Design and made it to 4-wheeler:
From the principal model “Model 1” as he called it Benz created two differences. He sent “Model 2” in the late spring of 1888 to Hofwagenfabrik Theodor Wecker in Offenbach, where it changed over into a four-wheeled vehicle. Benz was not happy with the outcome, thus the vehicle was dispatched to a shed without being placed into administration[2].
Variation in Design of Model-3:
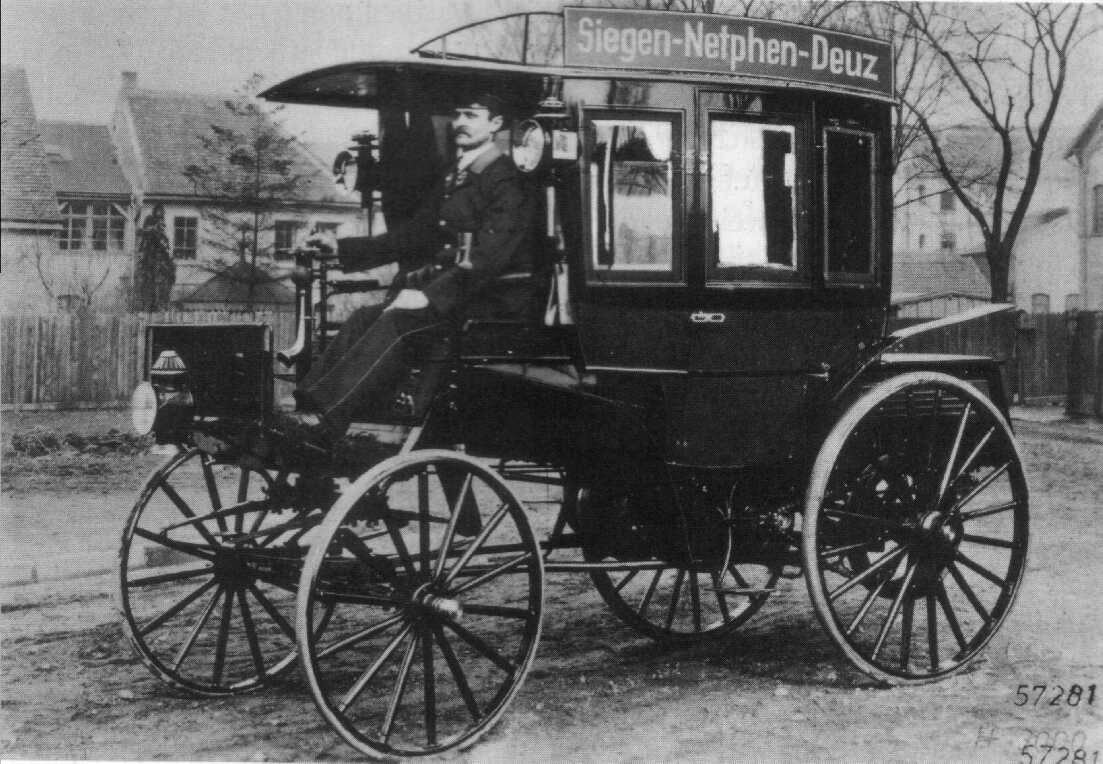

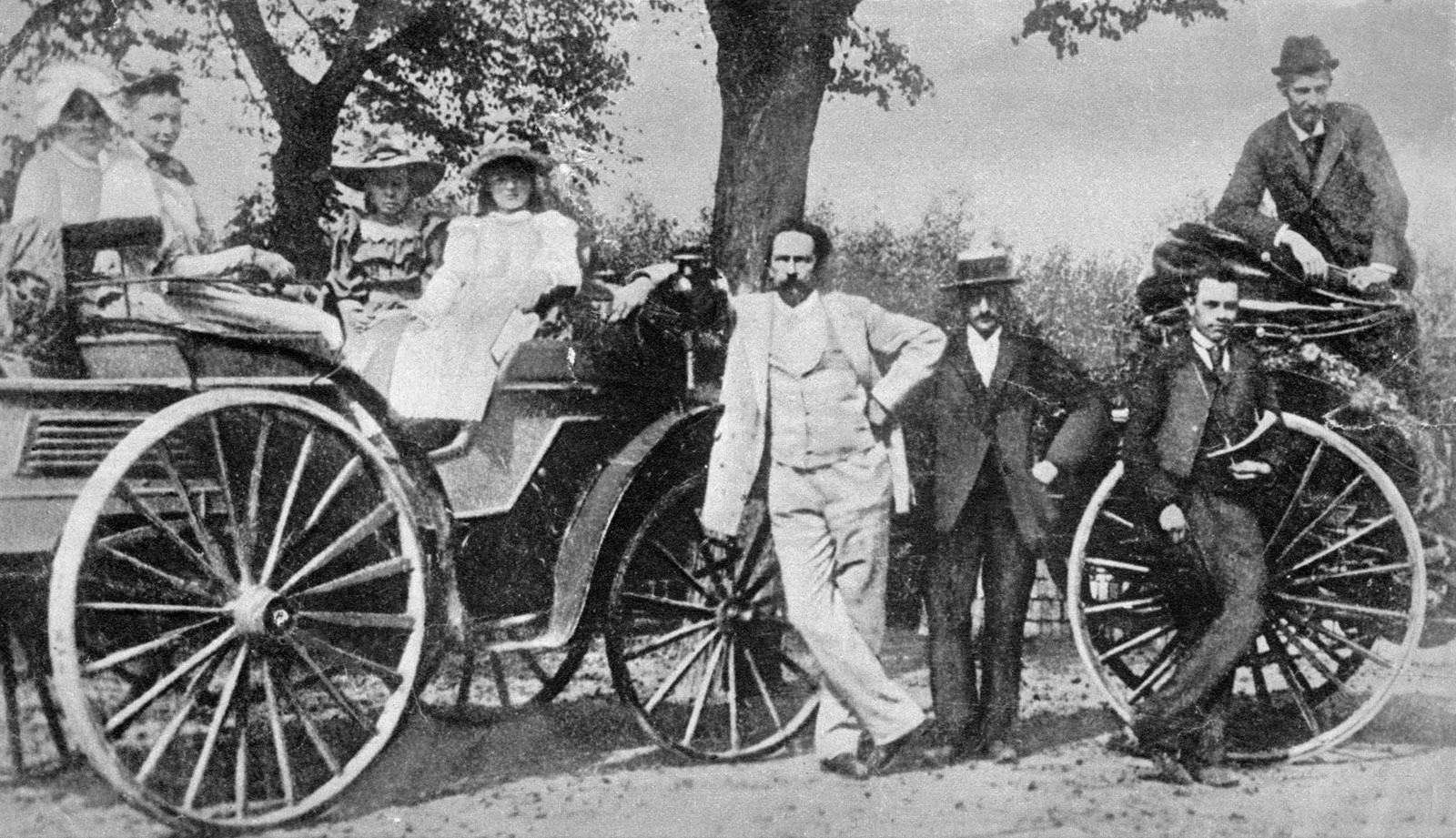
A significant achievement, then again, was “Model 3”, which had rough wooden talked wheels rather than delicate-looking wire rods and likewise outfitted with an even more extraordinary motor. It was with this variation that Bertha Benz comprised her incredibly significant distance venture in August 1888, the first in-car history.
Joined by her children Richard and Eugen and unbeknown to her better half. She set off from Mannheim to project out to Pforzheim, 100 kilometers away, to visit her mom. With this tour, she verified the car’s rationality for regular use and encouraged her better half’s opinion that his arrangements were all around established [2].
Munich Engineering Exhibition:
In September 1888, half a month after the incredible tour, Benz introduced his development to a bigger mass at the Munich Engineering Exhibition. The press distributed point-by-point reports about the trials in which he was involved with the Patent Motor Car between the show grounds and the city a few times every day. The panel of the show introduced the Grand Gold Medal, the most notable honor, to the Patent Motor Car. Thus “Model 3” turned into the world’s first arrangement delivered vehicle. While the vehicle was the subject of just restricted interest in Germany, it caught the creative mind of the French public. Carl Benz moved the passage rights there to French designer Émile Roger, who was at that point selling Benz fixed motors in France [2].
Thinking About Future Possibilities:
His business partners Rose and Eslinger was progressively nervous about the future possibilities of the Benz development. Carl Benz again ended up standing up with the need to discover new speculators. In May 1890, Julius Ganß and Friedrich von Fischer replaced Rose and Eslinger. On splitting, Rose offered Benz the all-around minor bit of guidance: “I’d disregard the engine vehicle on the off chance that I was you”. With the appearance of the new investors, Rheinisch Gasmotoren-Fabrik Benz and Cie. had the option to develop into the second biggest motor production line in Germany, getting concurrently the major motivation for car improvement [2].
New Vehicle “Velo” and The Cortana Motors:
In February 1893 Carl Benz licensed his double rotation engine, with which he had regarding attempted the controlling issue. It was his initial four-wheeled engine vehicles, the Victoria and the Vis-à-vis.
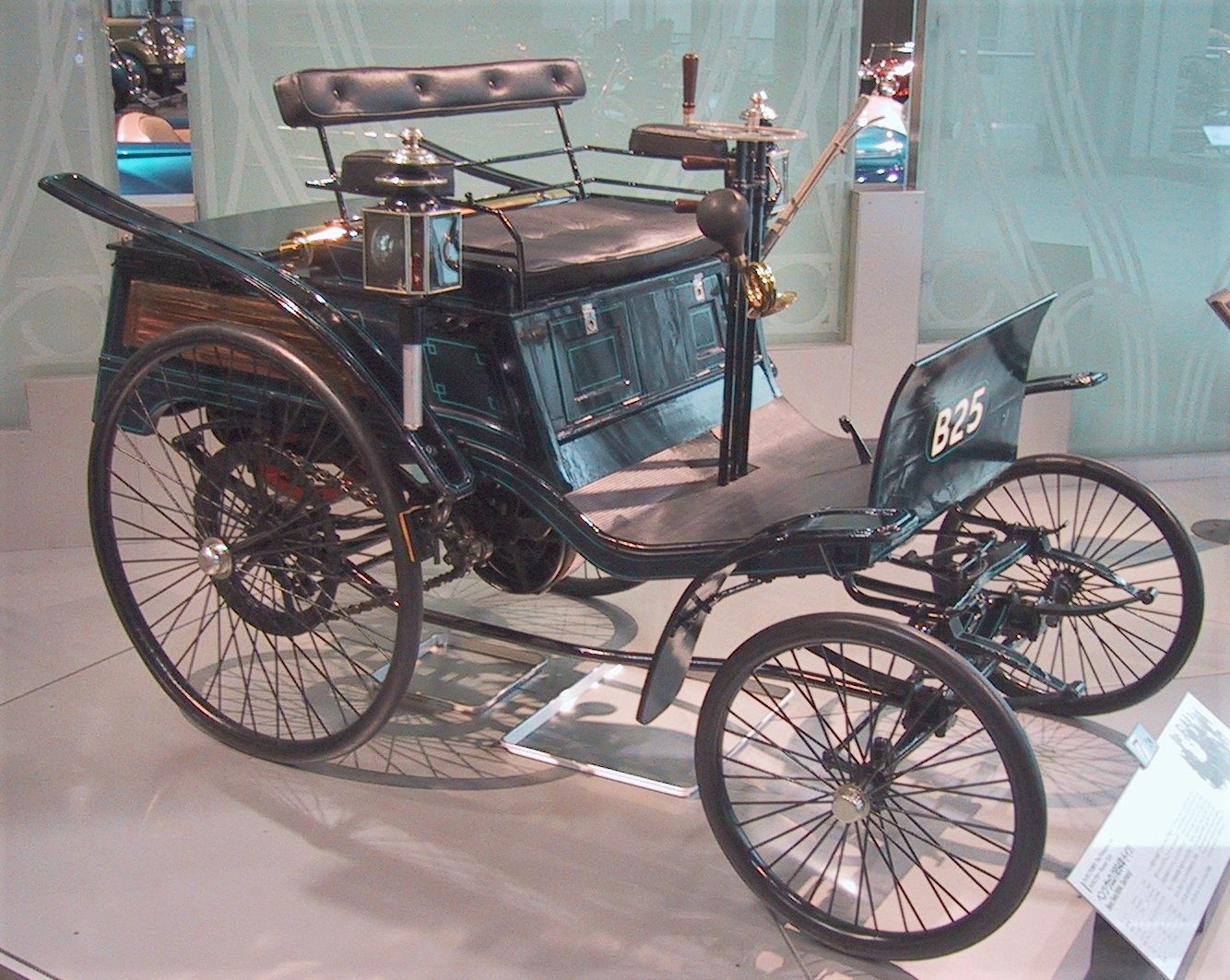

The vehicle with which they accomplished the forward hop to higher marketing projections was the four-wheeled Motor Velocipede, called “Velo” for short, which worked from 1894 to 1901. This was an attractive, evaluated light vehicle for two people. Given that a collective of 1200 units built, they view it as the main volume-made car[2].
In 1897 Benz built up the “Contra motor”, the ancestor of the present on a level plane limited motor. With it the organization prevailing regarding satisfying the developing interest for more powerful vehicles. In the very year, they set the main German vehicle club up in Berlin. The establishing individuals included both Carl Benz and Gottlieb Daimler [2].
Benz and Cie Car Production:
The basic meeting on 30th September 1897 is maybe the major event on which the two-car pioneers were in a similar spot at the same time. Benz reviewed: “I never addressed Daimler in for my entire life. When I saw him in Berlin, in a good way. As I drew nearer–I would have gotten a kick out of the chance to have made his colleague, before he vanished in the group. [2]“
Benz and Cie. formed into the world’s driving car produced by the turn of the century. In May 1899, they changed the organization into a stock partnership. Julius Ganß, an assistant since 1890, delegated to the Board of Management together with Carl Benz and assumed control over the business of the executives. The labor force in vehicle creation developed from 50 specialists in 1890 to 430 every 1899. The organization fabricated 572 vehicles in the 1899 monetary year and created 603 the year after. Shortly after the turn of the century, a difficult period began for Benz & Cie.: cheaper and more powerful vehicles notably from France enjoyed considerably greater commercial success than the Benz cars, which were designed mainly for long-distance operation and rather leisurely speeds[2].
Redefined Mercedes Benz:
The 35 hp Mercedes had completely redefined the automobile in early 1901 and had become the example for many other manufacturers. Compared to the Mercedes models from Cannstatt, the Benz motor cars suddenly looked antiquated. The unit sales of Benz & Cie. declined to 385 vehicles in the 1901 financial year, falling even further the following year to 226 units[2].

Since Carl Benz stuck to his previous designs, especially the belt drive, Julius Ganß seized the initiative. He hired a team formed around the French design engineer Marius Barbarou to develop a new model range. A “German engineering office” headed by chief design engineer Georg Diehl competed with this “French engineering office” to see who had better designs for future Benz models[2].
This discord in particular in his very own sphere, the design of automobiles was too much for Carl Benz: in January 1903, the 58-year-old Benz finished his active work for the company. His sons Eugen and Richard left with him. In 1904, however, Carl Benz had himself appointed to the Managerial Board of the company he had founded, and Richard Benz returned to Mannheim as head of passenger car production. The new model policy bore fruit, and after posting losses in the 1903 financial year, the business was back on the road to success again in 1904[2].
Organization by Carl Benz:
In 1906 Carl Benz set up the organization “Carl Benz Söhne” in Ladenburg, the town between Heidelberg and Weinheim, which had been home to the Benz family since 1905. Owned by Carl Benz and his son Eugen, they originally intended the new company to produce gas-fired naturally sounded engines based on a design by Eugen Benz. However, growing competition from electricity and stationary diesel engines meant that the market for such engines had all but disappeared. The company. Therefore, he switched to vehicle manufacturing in 1908. In the same year, Richard Benz finally left Benz & Cie. for good and joined his father and his brother Eugen Benz in managing the business in Ladenburg[2].
Retirement of Carl Benz:
In 1912 Carl Benz retired as a shareholder and left the management only in the hands of his sons. Production continued until 1923, but in all only about 350, “Carl Benz Söhne” cars ever built [2].
Development of the Benz Company:
Carl Benz lived to see the development of motorized road transport and the final innovation of his idea.

On his 80th birthday the “once mocked and unrecognized inventor” as he saw himself in survey enjoyed the honors discussed on him from all over the world. Ten years earlier the Karlsruhe Technical University had awarded him an honorary doctorate, and in 1926 he was the first person to be given the freedom of the town of Ladenburg.
The Baden State Ministry awarded Carl Benz the Baden State Medal in Gold in 1928[2].
Death of Carl Benz:
In the last years of his life, 1926 to 1929, Carl Benz was even a member of the Supervisory Board of the new Daimler-Benz AG. On 4th April 1929, the automotive pioneer passed away at his home in Ladenburg. Bertha Benz, also highly admired, lived on until 5th May 1944. Today the home of the Benz family is a museum and the seat of the “Daimler and Benz Foundation” established in 1986[2].
References:
1. Wikipedia. 10th December 2020; Available from: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carl_Benz.
2. mercedes-benz-publicarchive. 10th December 2020; Available from: https://mercedes-benz-publicarchive.com/marsClassic/en/instance/ko/Carl-Benz.xhtml?oid=580.